As summer approaches, many of us look forward to longer days and sun-filled activities. However, it's crucial to remember the risks associated with excessive sun exposure. While sunburns are a common concern, a more severe condition is often overlooked: sun poisoning. Unlike sunburn's typical redness and discomfort, sun poisoning symptoms can be more intense and sometimes dangerous.
What Is Sun Poisoning?
Sun poisoning doesn't involve actual poisoning. Think of it as an extreme sunburn after prolonged exposure to harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays, especially without adequate protection. This condition is more likely to affect individuals with fair skin and those with a family history of skin cancer. Understanding the distinction between regular sunburn and sun poisoning is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.

Marcus Silva/Pexels | Sun poisoning is more likely to affect individuals with fair skin and those with a family history of skin cancer.
The Symptoms of Sun Poisoning
Identifying sun poisoning is key to managing its effects. Initially, it may seem like a normal sunburn, marked by redness and slight discomfort. However, as the condition progresses, the symptoms become more severe.
Intense Skin Redness and Pain
The first indication of sun poisoning is often an unusually intense redness and pain in the affected areas. This pain is generally more severe than what is experienced with a typical sunburn and can feel deep and throbbing. The skin may also feel hot, and slight pressures or touches can be disproportionately painful.
Blistering or Peeling Skin
Unlike ordinary sunburn, sun poisoning can cause blistering or peeling skin shortly after exposure. These blisters may be large and painful, and the peeling can be extensive, indicating deeper skin damage. This symptom underscores the severity of the burn and the body's attempt to heal by shedding damaged cells.
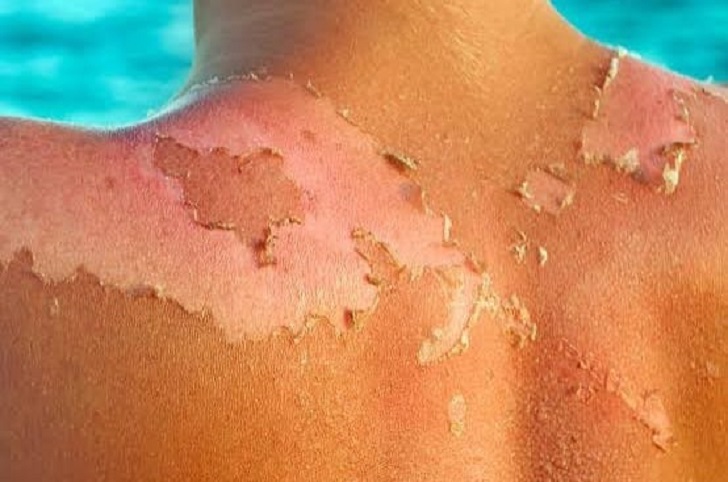
@debbiebiyemiadewumi | Instagram | Sun poisoning can cause blistering or peeling skin shortly after exposure.
Systemic Symptoms: Fever, Chills, Nausea, and Headaches
Sun poisoning can also manifest systemic symptoms that affect the entire body. Victims may develop a fever and chills as the body reacts to the severe sun damage. Nausea and headaches are also common, reflecting the body's overall distress and response to inflammation caused by UV exposure.
Dehydration and Dizziness
Dehydration is a direct consequence of extended sun exposure, especially if preventive measures like drinking water are neglected. This dehydration can lead to dizziness, fainting, or a light-headed feeling, complicating the body's ability to recover and increasing the risk of further health issues.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many sun poisoning cases can be treated at home, there are times when medical intervention is necessary. If you experience severe symptoms like facial swelling, blistering over a large area, or systemic symptoms like headache and dizziness, it's important to seek professional help. Medical treatments may include IV fluids to address dehydration and electrolyte imbalances and prescription medications to prevent infection and manage pain.

Freepik | While many sun poisoning cases can be treated at home, there are times when medical intervention is necessary.
Effective Prevention Strategies for Sun Poisoning
Preventing sun poisoning doesn't require extraordinary measures. The steps to prevent it are similar to those for avoiding sunburns:
- Use Broad Spectrum Sunscreen: Opt for a sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 that offers broad-spectrum protection, guarding against both UVA and UVB rays. Apply it 15 minutes before going outside and reapply every two to four hours or immediately after swimming or sweating.
- Limit Sun Exposure: The sun's rays are strongest between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m. Plan your outdoor activities outside these hours if possible.
- Wear Protective Clothing: A wide-brimmed hat, sunglasses, and long-sleeved shirts can provide additional protection.
- Be Mindful of Medications: Some medications, like certain antibiotics, heart medications, and acne treatments, can increase your sensitivity to sunlight. If you're taking any of these, you may need to take extra precautions.
By understanding and recognizing the distinct symptoms of sun poisoning, you can take proactive steps to enjoy your summer safely. Whether you're heading to the beach or just spending time outdoors, keep these tips in mind to protect yourself and your family from the potentially severe effects of sun poisoning.








